工厂设计模式(Factory Pattern)是一种很常见的设计模式,属于创建型模式,主要作用就是来创建对象。
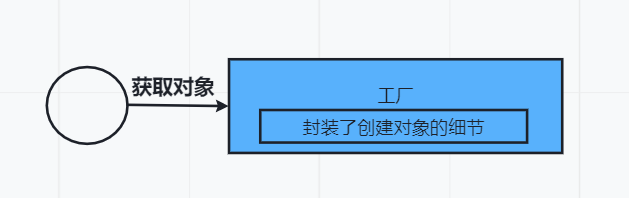
简单工厂模式
原理图
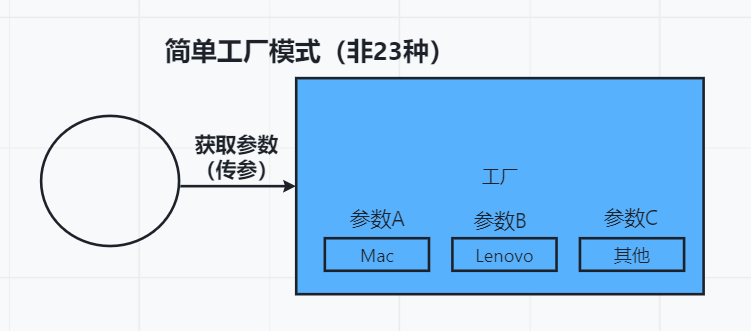
举个栗子
新建一个只提供返回品牌的接口。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| package com.heifan.design.patterns.factory;
public interface LaptopI {
String brand();
}
|
实现接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class LenovoLaptop implements LaptopI {
@Override
public String brand() {
return "Lenovo";
}
}
public class MacLaptop implements LaptopI {
@Override
public String brand() {
return "Mac";
}
}
|
简单的工厂类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public class LaptopFactory {
public static LaptopI createLapTop(String brand){
switch (brand){
case "Lenovo":
return new LenovoLaptop();
case "Mac":
return new MacLaptop();
default:
return null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LaptopI mac = LaptopFactory.createLapTop("Mac");
String brand = mac.brand();
System.out.println(brand);
}
}
|
工厂设计模式
超类
超类可以是接口、抽象类、父类。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public abstract class Computer {
public abstract String getRAM();
public abstract String getHDD();
public abstract String getCPU();
@Override
public String toString() {
return "RAM= "+this.getRAM()+", HDD="+this.getHDD()+", CPU="+this.getCPU();
}
}
|
子类
子类 PC 和 Server 实现了 Computer:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public class PC extends Computer{
private String ram;
private String hdd;
private String cpu;
public PC(String ram, String hdd, String cpu){
this.ram=ram;
this.hdd=hdd;
this.cpu=cpu;
}
@Override
public String getRAM() {
return this.ram;
}
@Override
public String getHDD() {
return this.hdd;
}
@Override
public String getCPU() {
return this.cpu;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public class Server extends Computer{
private String ram;
private String hdd;
private String cpu;
public Server(String ram, String hdd, String cpu){
this.ram=ram;
this.hdd=hdd;
this.cpu=cpu;
}
@Override
public String getRAM() {
return this.ram;
}
@Override
public String getHDD() {
return this.hdd;
}
@Override
public String getCPU() {
return this.cpu;
}
}
|
工厂类
基于相同的参数类型,返回了不同的对象:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class ComputerFactory {
public static Computer getComputer(String type, String ram, String hdd, String cpu) {
if ("PC".equals(type)) {
return new PC(ram, hdd, cpu);
}else if ("Server".equals(type)){
return new Server(ram, hdd, cpu);
}
return null;
}
}
|
测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public class TestFactory {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Computer pc = ComputerFactory.getComputer("PC", "2 GB", "500 GB", "2.4 GHz");
Computer server = ComputerFactory.getComputer("Server", "16 GB", "1 TB", "2.9 GHz");
System.out.println("Factory PC Config::" + pc);
System.out.println("Factory Server Config::" + server);
}
}
|
输出:
1
2
| Factory PC Config::RAM= 2 GB, HDD=500 GB, CPU=2.4 GHz
Factory Server Config::RAM= 16 GB, HDD=1 TB, CPU=2.9 GHz
|
工厂设计模式的优点
面向接口编程,体现了面向对象的思想;
将创建对象的工作转移到了工厂;
JDK中的工厂设计模式
- java.util.Calendar, ResourceBundle and NumberFormat getInstance() 使用了工厂方法模式;
- valueOf() 在包装类中,如Boolean, Integer 也使用了工厂方法模式;

